PS: This is a slightly updated copy of this page
With this editor
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
2. Functional Objectives
3. Non-Functional Objectives
4. Context Model
Goal Statement
Context Diagram
System Externals
5. Use Case Model
System Use Case Diagram
Use Case Descriptions
Login User
Register User
Register Preferences
Place Order (Customer)
(Sales Agent)
Charge Customer
Bill Customer
Request Assistance
6. Class Model
7. DB Design
8. Wire Frames
9. Appendix
1. Introduction
1.1 Purpose of Document
This is a Requirements Specification document for a new web-based
sales system for Solar Based Energy, Inc. (SBE). SBE is a distributor of
alternative energy products including windmills, photovoltaics and
fuel cells. The new system will upgrade the current websites to
provide customers and employees customized browsing of the product
catalog and the ability to complete product orders on-line. This document
describes the scope, objectives and goal of the new system. In addition
to describing non-functional requirements, this document models the functional
requirements with use cases, interaction diagrams, and class models. This
document is intended to direct the design and
implementation of the target system in an object oriented language.
1.2 Project Summary
| Project Name: | SBE Sales System |
|---|
| Project Manager: |
Mary Beth Lohse, CEO, CIS 616 Consulting |
|---|
| Project Analysts: |
Benjamin B. Bolz, Lead Analyst
Cynthia C. Caldwell, Senior Analyst
David D. Dreese, Analyst
Helen H. Hitchcock, Analyst |
|---|
| Responsible Users: |
Imogene I. Ives, President of SBE
Benjamin B. Baker, Vice-President of Sales |
|---|
1.3 Background
SBE sells state-of-the-art alternative energy systems utilizing
wind and solar power. SBE customers include both individuals and
businesses interested in incorporating wind or solar energy sources
into either new or existing construction. SBE has identified two
trends that they believe will cause explosive growth in the demand
for their products. The first is the continuing energy crisis in
the western United States. The second is the maturation of fuel
cell technology which provides a feasible system for storing excess
power generation for later use.
SBE sells state-of-the-art alternative energy systems utilizing
wind and solar power. SBE customers include both individuals and
businesses interested in incorporating wind or solar energy sources
into either new or existing construction. SBE has identified several
trends that they believe will cause explosive growth in the demand for their
products. They include the growing consumer unease with deregulated energy
markets, the potential for disruptions to energy imports, and the maturation
of fuel cell technology which
provides a feasible system for storing excess power
generation for later use.
Because of the innovative and technical nature of their products,
SBE employs sales agents who can guide customers through the
process of choosing an alternative energy system.
Other SBE employees are identified as a product "owners". The product
owner is the expert on a particular product or product line.
As the authoritative source of product information he produces
whitepapers--highly technical and focused documents on product
specifications.
As alternative energy becomes more mainstream,
SBE anticipates changes in the needs of their customers.
Some customers will be more knowledgeable
and will need less assistance from a sales agent.
Expanding sales outside the United States will drive the
need to service customers in languages other than English.
Currently there are two separate web sites. The public website
(www.sbe.com) is static HTML. It provides general information
about SBE and its products. Customers who are interested in
ordering are provided contact information for the nearest
SBE sales office. The internal website (www.sbesales.com) is restricted
to SBE employees and provides detailed product information. Sales orders
are placed by agents on this site. Two different Oracle databases underly
these sites.
Problems with the current system include
- the information available on the public website is too limited
and the user cannot immediately place an order
- the existence of two databases means information is often
inconsistent or incorrect
- users who need more technical information have difficulty accessing
the relevant whitepapers
- sales agents have difficulty reaching product owners
Imogene I. Ives,
President of SBE has requested that an analysis be done with a view to
reengineering the current sales system.
The new system should allow customers direct access to product
information and ordering as well as continuing to provide support to
the existing sales agent network.
1.4 Project Scope
The scope of this project is a web-based system that supports the
marketing of SBE products directly
to customers as well as through the existing sales agent network.
Advertising of products, inventory control,
and account billing are not part of this project.
The two current web sites will be replaced by this new system. In addition,
changes to the logical and physical design of the current databases
are expected. The actual implementation of a new database system is not
part of this project. A web search engine and language translator will
be obtained as purchased components for the new system. Their internal
details are not part of this project. Issues of website security, other
than password protection within the site, are not part of this project.
1.4.1 USP compared to competitor products
Competitors providing closest similar services are
- http://www.competitor1.com/ : Expensive. Not all services may not be required by small firms. We could provide only required services at cheaper rate.
- http://www.competitor2.com/ : Not all services are available.
1.5 System Purpose
1.5.1 Users
Those who will primarily benefit from the new system and those who
will be affected by the new system include
- Customers:
- Upon implementation of the new system, customers will
find site navigation, product identification and product
ordering easier. Customers will be able to choose whether
to buy directly from SBE or work with a sales agent.
- Sales Agents:
- The new system will provide sales agents with more detailed,
accurate and up-to-date product information. They will be
informed of potential customers more quickly and they will
have faster access to the product owner.
- Product Owners:
- Product owners will be allowed to maintain the data about
their products directly. This will eliminate delays in
getting new products or changed product specifications into
the system.
- Customer Service Department:
- The new system should reduce the workload of Customer Service
as customers are able to find the information they need from
the web-site.
- Marketing Department:
- Site navigation data could be sent to the Marketing
Department. Understanding how a customer uses the web site
to make a purchase will result in improvements in getting
and keeping customers.
- Accounting Department:
- Purchase information will be sent directly to Accounting,
allowing for more accurate and timely billing.
- Shipping Department:
- Purchase information will be sent directly to Shipping
for inventory control and order processing.
- Information Technology Department:
- This department will be responsible for implementing the
new database, hosting the website and maintaining the system.
1.5.2 Location
The system will be available to any potential customer using the
Internet. SBE employees may also use the system from any location
and will be able to access restricted areas of the site through a password
protection scheme.
1.5.3 Responsibilities
The primary responsibilities of the new system:
- provide customers direct access to up-to-date, accurate
product information on which they can make a decision
to buy
- customize product offerings to specific users
- allow differential access to web pages based on
type of user
- allow customers to place an order through the website
- allow customers to request the assistance of a sales agent
- provide sales agents improved access to product information
and product owners
- allow product owners to maintain information about their
products directly
- allow access to whitepapers on demand
- send order information directly to Accounting and Shipping
Other desired features of the new system:
- a consistent "look and feel" throughout the website
- full-text searches of the web pages a user has permission
to access
- on-line help in website navigation
- password protection scheme for non-public web pages
- translation of a web page to another language
The system will not be responsible for account receivables,
or inventory control.
1.5.4 Need
This system is needed in order to service the expected increase in
demand for alternative energy products. Replacement of the current
websites will eliminate the shortcomings of those sites. The new
system will allow SBE to rapidly increase sales without a large
and expensive increase in the number of sales agents and other
customer support employees.
1.6 Overview of Document
The rest of this document gives the detailed specifications for the
new sales system. It is organized as follows:
- Section 2: Functional Objectives
Each objective gives a desired behavior for the system, a business
justification, and a measure to determine if the final system has
successfully met the objective. These objectives are organized by priority.
In order for the new system to be considered successful, all high
priority objectives must be met.
- Section 3: Non-Functional Objectives
This section is organized by category. Each objective specifies
a technical requirement or constraint on the overall characteristics
of the system. Each objective is measurable.
- Section 4: Context Model
This section gives a text description of the goal of the system, and a
pictorial description of the scope of the system in a context diagram.
Those entities outside the system that interact with the system are described.
- Section 5: Use Case Model
The specific behavioral requirements of the system are detailed in
a series of use cases. Each use case accomplishes a business task
and shows the interaction between the system and some outside actor.
Each use case is described with both text and an interaction diagram.
An interface prototype is also shown.
The system use case diagram depicts the interactions between all
use cases and system actors.
- Section 6: Class Model
A class is a collection of objects in the system that have the
same data and behavior.
All analysis classes and their relationships are shown on the
class diagram.
- Section 7: An appendix containing a glossary that
defines terms specific to this project
2. Functional Objectives
2.1 High Priority
- The system shall allow for on-line product ordering by either
the customer or the sales agent. For customers, this will eliminate
the current delay between their decision to buy and the placement
of the order. This will
reduce the time a sales agent spends on an order by x%.
The cost to process an order will be reduced to $y.
- The system shall reflect a new and changed product description within
x minutes of the database being updated by the product owner. This will
reduce the number of incidents of incorrectly displayed information by x%.
This
eliminates the current redundant update of information, saving $y dollars
annually.
- The system shall display information that is customized based
on the user's company, job function, application and locale. This feature will
improve service by reducing the mean number of web pages a user
must navigate per session to x. It should reduce unnecessary phone
calls to sales agents and staff by x%.
- The system shall allow employees to view the owner of any product.
An employee should be able to contact the correct owner
in one phone call x% of the time.
- The system shall allow a customer to directly contact the nearest sales
office in his region. This will improve service by reducing the time
to respond to a customer request to no more than x days.
- The system shall provide accounting with accurate purchase transaction
data. This will improve customer service by reducing billing complaints
by x% and save $y in correcting inaccurate accounts.
- The system shall provide shipping with accurate order data. This will
allow the order to be processed in x days and inventory to be updated
within y hours.
2.2 Medium Priority
- The system shall provide a search facility that will allow full-text
searching of all web pages that the user is permitted to access. The
system must support the following searches:
- find all words specified
- find any word specified
- find the exact phrase
- Boolean search
- The system shall make whitepapers available from the product page.
This will allow customers to
answer product questions themselves, reducing customer support
costs by $x annually.
2.3 Low Priority
- The system shall allow the user's status to be stored for the
next time he returns to the web site. This will save the user x minutes
per visit by not having to reenter already supplied data.
- The system shall provide marketing with customer navigation
information. This information will allow marketing to determine
what information prompts a purchase and help target potential
customers more effectively. This will increase annual revenue
by $x in additional sales.
- The system shall translate web pages into the languages of
the countries where the company's products are available. This
will improve customer service and reduce the number of support
calls from foreign customers by x%.
3. Non-Functional Objectives
3.1 Reliability
- The system shall be completely operational at least x% of
the time.
- Down time after a failure shall not exceed x hours.
3.2 Usability
- A sales agent should be able to use the system in his
job after x days of training.
- A user who already knows what product he is interested in should
be able to locate and view that page in x seconds.
- The number of web pages navigated to access product information
from the top page should not exceed x.
3.3 Performance
- The system should be able to support x simultaneous users.
- The mean time to view a web page over a 56Kbps modem connection
shall not exceed x seconds.
- The mean time to download and view and whitepaper in PDF format
for a 56Kbps modem shall not exceed x seconds.
3.4 Security
- The system shall provide password protected access to web pages that
are to be viewed only by employees.
- Transaction data must be transmitted in encrypted form.
3.5 Supportability
- The system should be able to accommodate new products and
product lines without major reengineering.
- The system web site shall be viewable from Internet Explorer 4.0
or later, Netscape Navigator/Communicator 3.0 or later and the America Online
web browser version 3.0 or later.
3.6 Online user Documentation and Help
- The system shall provide a web page that explains how to
navigate the site. This page should be customized based on
what pages that user is allowed to access.
- This help page should be accessible from all other pages.
3.7 Purchased Components
- A language translation tool from English to French and English to German
will be needed.
- A web site search engine will be needed.
3.8 Interfaces
The system must interface with
- The current Oracle database systems for product and
order information
- The current Oracle Financial accounting system
- The current AccountPro inventory system
- The acquired language translation tool
- The acquired web site search engine
4. The Context Model
The goal of the system is to allow SBE to increase sales revenue by x%
over the next y years with only a z% increase in sales and customer
service staff by
- allowing complete and accurate customer and order information
to be captured directly from the customer as well as from
sales agents
- providing customers and sales agents fast access to up-to-date and
accurate product information and whitepapers.
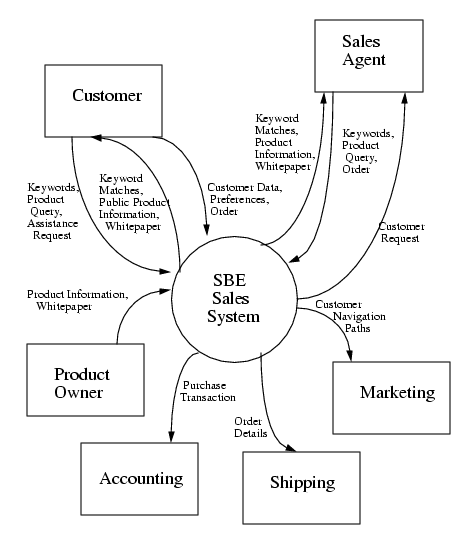
- Customer
- A customer is any user of the system that has not identified
himself as an SBE employee. A customer may search for public
product information by keyword, access whitepapers for a
particular product, order a product or request assistance
from a sales agent.
A customer who provides personal information
will get search and query results customized to his preferences.
- Sales Agent
- A sales agent is a user who has been verified as an SBE
employee. A sales agent may access all available product
information and whitepapers, including the product owner.
A sales agent may place an order on behalf of a customer.
He will be informed by the
system of any customers in his region who have requested
assistance.
- Product Owner
- The product owner is a user who has been verified as an
SBE employee. The product owner may update product information
and whitepapers for those products for which he is responsible.
- Accounting
- The Accounting department is responsible for all SBE financial
transactions. The Accounting department is informed of
all purchases and is responsible for later collection of
accounts receivable.
- Shipping
- The Shipping department is informed of purchases so that
it can process the order and update inventory.
- Marketing
- The Marketing department is responsible for creating demand
for SBE products. It will receive website navigation data
to use in planning marketing strategies.
5. The Use Case Model
more examples
eg:
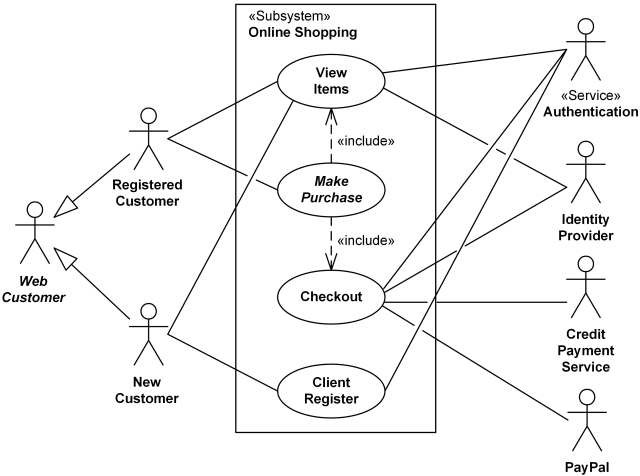 Notes:
Notes:
- For all use cases, the user can cancel the use case at
any step that requires user input. This action ends the
use case. Any data collected during that use case is lost.
- For all use cases that require a logged in user, the current
login session is updated during the use case to reflect the
navigation paths through the use case.
| Use Case Name: |
Login User |
| Summary: |
In order to get personalized or restricted information, place orders
or do other specialized transactions a user must login so that
that the system can determine his access level. |
| Basic Flow: |
- The use case starts when a user indicates that he wants to login.
- The system requests the username and password.
- The user enters his username and password.
- The system verifies the username and password against all registered
users.
- The system starts a login session and displays a welcome message based on
the user's preferences.
|
| Alternative Flows: |
- Step 4:
- if username is invalid, the use case goes back to step 2.
- Step 4:
- if the password is invalid the system requests that the
user re-enter the password. When the user enters another password
the use case continues with step 4 using the
original username and new password.
|
| Extension Points: |
none |
| Preconditions: |
The user is registered. |
| Postconditions: |
The user can now obtain data and perform functions according
to his registered access level. |
| Business Rules: |
Some data and functions are restricted to certain types of users
or users with a particular access level. |
| Use Case Name: |
Register User |
| Summary: |
In order to get personalized or restricted information, place orders
or do other specialized transactions a new user must register a username and password. |
| Basic Flow: |
- The use case start when a user indicates that he wants to register.
- The system requests a username and password.
- The user enters a username and password.
- The system checks that the username does not duplicate any
existing registered usernames.
- The system requests a name (*),
street, city, state, zipcode(*), phone and email address. Items
marked by (*) are required.
- The user enters the information.
- The system determines the user's location and access level and
stores all user information.
- The system executes use case Register Preferences.
- The system starts a login session and displays a welcome message based on
the user's preferences.
|
| Alternative Flows: |
- Step 4: If the username duplicates an existing username
the system displays a message and the use case goes back to step 2.
- Step 5: If the user does not enter a required field, a message
is displayed and the use case repeats step 4.
|
| Extension Points: |
Register Preferences |
| Preconditions: |
none |
| Postconditions: |
The user can now obtain data and perform functions according
to his registered access level. |
| Business Rules: |
- A registered user's location is the SBE location nearest his
zip code.
- Access levels are
- 0: A user can access only data classification 0
- 1: The user can access data classification <= 1
- 2: The user can access data classification <= 2
The default access level is 0.
|
| Use Case Name: |
Register Preferences |
| Summary: |
This use case allows a registered user to enter or change his
preferences. |
| Basic Flow: |
- The use case start when a user indicates that he wants to enter
or modify his preferences.
- The system displays all current product lines. It indicates
any product lines that the user has currently selected.
- The user selects/deselects product lines.
- The system displays current language preferences. It indicates
the language preference currently selected.
- The user may select a different language preference.
- The system stores any change to language preference.
|
| Alternative Flows: |
none
|
| Extension Points: |
none |
| Preconditions: |
The user is logged in. |
| Postconditions: |
The system can customize a welcome message based
on the user's revised preferences. |
| Business Rules: |
Language selections allowed are are English (default),
French and German. |
| Use Case Name: |
Place Order
Scenario: Customer places his own order. |
| Summary: |
This use case allows a registered customer to place
an order for a product. |
| Basic Flow: |
- The use case start when a customer indicates he wants to
place an order for the current product being displayed.
- The system displays the customer's information: name,
street, city, zip, phone, email.
- The customer may add or change any of the information.
- The system stores any changes. If the zipcode has changed,
the system modifies the customer's location.
- The system requests the quantity to order and the shipping address.
- The customer enters quantity and shipping address.
- The system displays the payment options available to
this customer.
- The customer selects a payment option.
- The system completes the payment by executing
use case Charge Customer or Bill Customer
depending on which option was selected.
- The system stores the order information, decreases the
quantity on hand for the product and sends the
order details to Shipping.
- The system displays a order completion message and sends
a receipt to the user.
|
| Alternative Flows: |
- Step 9:
- If the selected payment method could not be
validated, go to step 8 to get
another payment option.
- Step 10:
- If the quantity on hand is not sufficient for
this order, a message is sent to the customer
and the use case is canceled.
|
| Extension Points: |
Charge Customer; Bill Customer |
| Preconditions: |
The customer is logged in and has completed a
search for the product to be ordered |
| Postconditions: |
The product is sold. |
| Business Rules: |
If a customer has been previously authorized for billing by a
sales agent, the customer may billed for the order. Otherwise
the customer must pay in full by credit card at the time
of the order. |
| Use Case Name: |
Place Order
Scenario: Sales agent places an order for a customer. |
| Summary: |
This use case allows a sales agent to place
an order for a registered customer. It also allows the
sales agent to change the customers access level and
payment options. |
| Basic Flow: |
- The use case starts when a sales agent indicates he wants to
place an order for a customer.
- The system requests the customers username.
- The sales agent enters the username.
- The system displays the registered customer's information,
including access level and payment options.
- The sales agent makes changes to the customer information.
- The system stores any updated information.
- The system requests the product id, quantity and shipping address.
- The sales agent enters the product id, quantity and shipping address.
- The system displays payment options for this customer.
- The sales agent selects a payment option.
- The system completes the payment by executing
use case Charge Customer or Bill Customer
- The system stores the order information, decreases the
quantity on hand for the product, sends the
order details to Shipping.
- The system displays a order completion message and sends
a receipt to the customer.
|
| Alternative Flows: |
- Step 11:
- If the selected payment method could not be
validated, go to step 10 to get
another payment option.
- Step 12:
- If the quantity on hand is not sufficient for
this order, a message is sent to the sales agent
and the use case is canceled.
|
| Extension Points: |
Charge Customer; Bill Customer |
| Preconditions: |
The sales agent is logged in, knows the username
of the customer, his payment method and the product
to be ordered. |
| Postconditions: |
The product is sold and the sales agent is credited with
the sale. |
| Business Rules: |
Sales agent have the authority to allow a customer to be
billed. They may also increase the customer's access
level to product data. |
| Use Case Name: |
Charge Customer |
| Summary: |
This use case charges the order currently being
placed to a credit card. |
| Basic Flow: |
- The use case begins when a user selects "Credit Card" as
a payment option, while in use case Place Order
- The system requests the credit card number, type and expiration
date.
- The user enters the information.
- The system verifies that the credit card is valid for the
amount to be charged and completes the credit card
transaction.
- The system stores the payment details and returns a
success message
|
| Alternative Flows: |
Step 4: If the credit card cannot be validated the
use case ends, returning a failure message |
| Extension Points: |
none |
| Preconditions: |
The system is executing use case Place Order. |
| Postconditions: |
The customer has been charged for the order. |
| Business Rules: |
Credit cards accepted are Visa, MasterCard and Discover. |
| Use Case Name: |
Bill Customer |
| Summary: |
This system gets the billing details for the
order. They will be part of the Daily Transactions
Report sent to Accounting in use case Report Daily
Transactions. Billing and collection is handled
outside this system by Accounting. |
| Basic Flow: |
- The use case begins when a user selects "Bill me" as
a payment option, while in use case Place Order
- The system requests the billing address.
- The user enters the billing address.
- The system stores the payment details.
|
| Alternative Flows: |
none |
| Extension Points: |
none |
| Preconditions: |
The system is executing use case Place Order and the
customer is authorized for billing. |
| Postconditions: |
Accounting can bill the customer for this order. |
| Business Rules: |
Customers can be billed if it was previously authorized
by a sales agent. |
| Use Case Name: |
Request assistance |
| Summary: |
This use case allows anyone using the web site to request
a contact from a sales agent. |
| Basic Flow: |
- The use case starts when the customer asks for assistance.
- The system displays all
product lines, and provides space for the customer to
type a (optional) question.
- The customer selects the product line(s) he is interested in
and may enter a question.
- The system asks for a name, email address and zip code.
- The customer enters name, email address and zip code.
- The system selects a sales agent based on the customer's
location and product lines selected in step 3.
- The system displays message informing the customer
of which agent will be in contact.
- The system sends the request information to the selected sales agent.
It stores the request information for registered customers.
|
| Alternative Flows: |
- Step 4:
- If the customer is registered and
has previously provided his name, email address and zip code
the use case skips to Step 6.
- Step 6:
- If the customer is registered and has previously
been assisted by a sales agent, that same agent is selected.
|
| Extension Points: |
none |
| Preconditions: |
none |
| Postconditions: |
The sales agent has the customer contact information. |
| Business Rules: |
Customers are assigned to a sales agent at the closest
SBE location whose specialties most closely match the
the product lines the customer has indicated. If there is more
than one such sales agent, the one with the fewest customer
assistance requests is selected. That sales agent continues to be
assigned to that customer for any future requests.
The actual contact between the sales
agent and the customer is outside the system. |
6. The Class Model
More examples
eg:
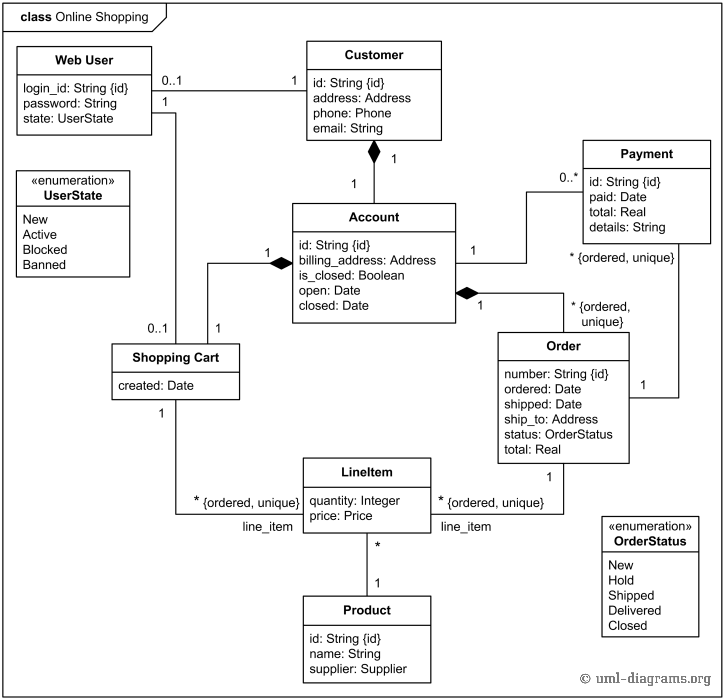

7. DB Design
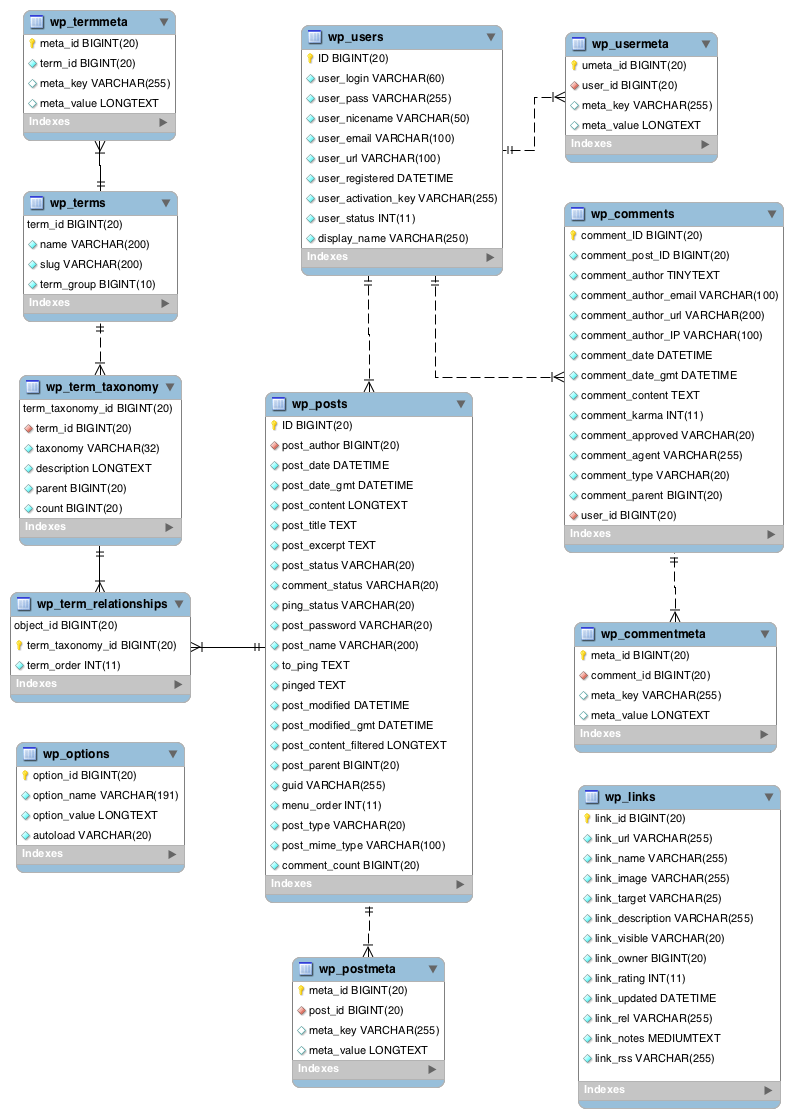
8. Wire Frames
9. Appendix
Glossary
- Whitepaper
- Technical paper containing detailed product specifications.





